Manual, Cobot and Robot Welding? How to Make the Choice?
Comparison of Robot and Cobot Welding
A robot is a high investment. The question must be asked how much production can be allocated to the welding robot and what its return on investment will be. Moreover, careful consideration must be given to where this robot will be installed, since these installations are usually fixed and moving of the setup afterwards is not always easy.
The flexibility is also limited: making adjustments in the program due to a change of the product to be welded is usually time consuming. The operators who will work with the welding robot must also receive a thorough training. Finally, a number of safety measures must also be taken. It is clear that for more complex products or for large series, the choice for a welding robot can be justified.
Robotic welding systems based on lightweight robots (the so-called “cobots”) remove many of the previously mentioned obstacles. A cobot is a small, compact, flexible and simple welding robot. The investment in a welding system with a lightweight cobot is relatively low. In addition, a cobot is transportable and can be mounted directly on a welding table, so that no special base has to be constructed. The initial training for operators can be limited to a few hours, to learn the basic functions, the setting options and the programming of straight, curved and round welds.
A safety cage like in the case for a welding robot is not a must, because the cobot arm automatically stops when it experiences a certain force. As a result, the entire installation remains compact and is perfectly mobile to implement, so that the cobot can be used at different locations.
A changeover to weld a new product usually takes less time because of the simple set-up, programming, and operation. The welding setup with clamps and fixtures can often simply remain on the welding table.
The flexibility due to the fast programming and simplicity of the cobot allows for a quick changeover from one component to another. Moreover, the lightweight cobot is perceived different by the employees, compared to a classic welding cell. A cobot is considered less as a competitor but rather as a reinforcement for the welder, a tool that helps the welders with their routine tasks. Economic considerations are of course decisive for a company. But in this respect, the lower investment costs in combination with the high availability are decisive for creating value for the company.

Figure 1 - Cobot welding at the Belgian Welding Institute.
Comparison Between Manual and Cobot Welding
The use of cobots does not always translate into worker replacement. According to Gil-Vilda et al [1], cobots are also the best solution for de-robotization challenges. Moreover, a collaborative robot can be descripted as "a robot designed to assist human beings as a guide or assistor in a constrained motion". It's worth mention that according to the American Welding Society, there is a global shortage of skilled welders [2].
Advantages of Cobots (over welding operators) are [2]:
- Robotics and automation can increase productivity, safety, quality, consistency of products;
- Cobots can work in hazardous environments (radiation, darkness, hot and cold, ocean bottoms, and so on);
- No need for environmental comfort like lighting, air conditioning, ventilation, noise protection;
- Continuous work;
- Repeatable precision at all times unless they wear out or something happens to them;
- Better accuracy;
- Cobots' accessories and sensor have better capabilities;
- Higher level of multitasking.
There are some disadvantages, though:
- Cobots replace human workers, causing economic hardship, worker dissatisfaction and resentment;
- Robots lack the capability to respond to emergencies, unless the situation is predicted, and the response is included in the system. Safety measures are needed to ensure that they do not injure operators and other machines that are working with them. This includes:
- Inappropriate or wrong responses
- Lack of decision-making power
- Loss of power
- Damage to the robot and other devices
- Injuries to humans
- Lower handicraft;
- Initial cost of equipment/installation [3]
On the other hand, manual welding has, of course, a lower initial cost and can benefit operators' adaptive intelligence, their handicraft and their flexibility. Aside from the aforementioned shortage of skilled operators, the disadvantages of manual welding are that years of training are needed to get proper skills and, of course, everything concerning exposure to dangerous environments. The main advantages and disadvantages for cobot and manual welding can be seen in Figure 1.
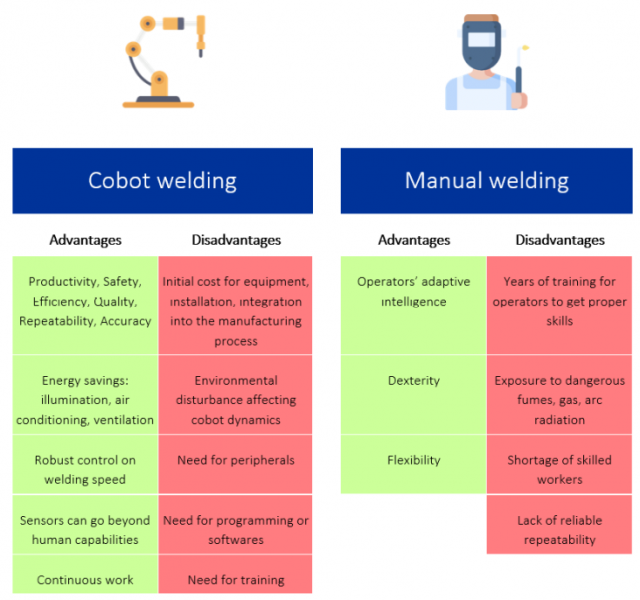
Figure 2 - The main advantages and disadvantages for cobot and manual welding.
References
[1] : Gil-Vilda, Francisco, et al. "Integration of a collaborative robot in a U-shaped production line: a real case study." Procedia Manufacturing 13 (2017): 109-115, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2017.09.015.
[2] : Dallos, Jennifer. “Combating the welder shortage”. 2017 Available: https://www.fabtechexpo.com/blog/2017/12/04/combating-the-welder-shortage
[3] : Smith, Alex MC, et al. "Novel hybrid adaptive controller for manipulation in complex perturbation environments." PloS one 10.6 (2015): e0129281, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0129281
Acknowledgements
The presented results were achieved within the project "Advanced Manufacturing Solution Tightly Aligned with Business Needs – AVANGARD". This project is funded by the European Union within the frame of the Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under Grant Agreement No. 869986
